Introduction to Display Ports
Display ports are essential connectors that facilitate the transfer of visual data from a computer or other digital device to a display monitor or screen. They serve as the bridge between your device and the monitor, enabling the transmission of images, videos, and other graphical content.

When it comes to connecting your GPU to a monitor, people think about Which Display Port to Use on GPU, choosing the right display port is crucial for optimal performance and visual experience. With various options available, such as HDMI, DisplayPort (DP), DVI, and VGA, selecting the most suitable one can be overwhelming. This article aims to provide insights into the different display ports available and help you make an informed decision on which display port to use on your GPU.
What are display ports?
Display ports are interfaces used to connect a GPU or graphics card to a display device, such as a monitor, TV, or projector. They transmit video and audio signals from the GPU to the display, allowing users to see images and videos on their screens.
Importance of choosing the right display port for GPU
Selecting the appropriate display port ensures compatibility between your GPU and display device, maximizing performance and enabling features such as high refresh rates, high resolutions, and adaptive sync technologies.
Types of Display Ports
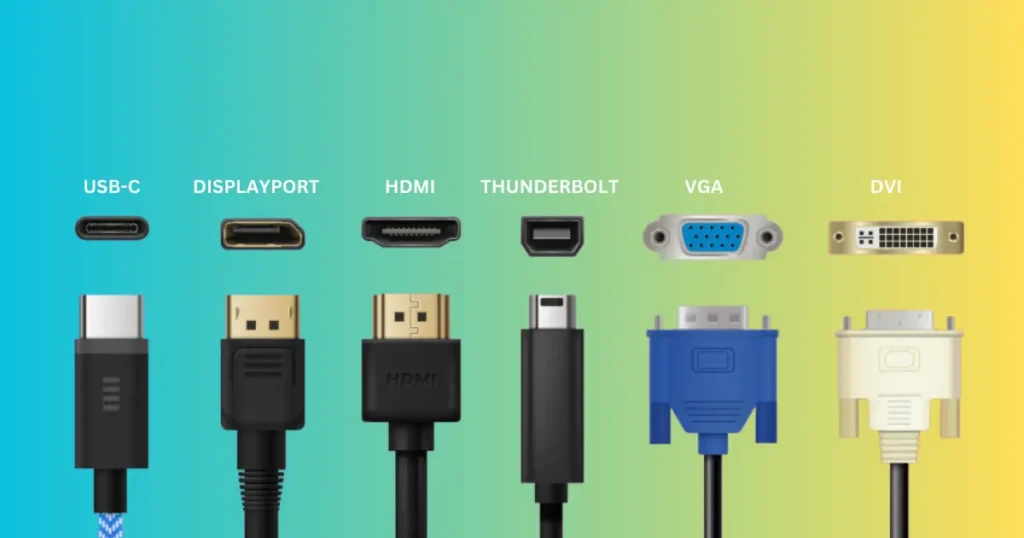

HDMI
HDMI (High-Definition Multimedia Interface) is a widely used digital interface for transmitting audio and video signals between devices. It supports high-definition video and audio formats, making it suitable for multimedia applications.
Advantages:
- Widely supported by various devices.
- Supports audio transmission.
- HDMI 2.1 offers high bandwidth for 4K and 8K resolutions.
Disadvantages:
- Limited refresh rates compared to DisplayPort.
- Less suitable for gaming and high-performance applications.
DisplayPort (DP)
DisplayPort is a digital display interface developed by the Video Electronics Standards Association (VESA). It offers high bandwidth and supports features such as high refresh rates, high resolutions, and adaptive sync technologies like AMD FreeSync and NVIDIA G-SYNC.
Advantages:
- High bandwidth for high resolutions and refresh rates.
- Supports adaptive sync technologies.
- Daisy-chaining multiple displays.
Disadvantages:
- Less common on consumer electronics compared to HDMI.
- Requires DisplayPort-compatible devices.
DVI
DVI (Digital Visual Interface) is an older digital video interface commonly found on older monitors and GPUs. It comes in several variants, including DVI-D (digital), DVI-I (integrated digital and analog), and DVI-A (analog). However, it lacks some features supported by HDMI and DisplayPort, such as audio transmission and adaptive sync.
Advantages:
- Compatible with older monitors and GPUs.
- Supports higher resolutions than VGA.
Disadvantages:
- Lack of audio support.
- Limited features compared to HDMI and DisplayPort.
VGA
VGA (Video Graphics Array) is an analog video interface widely used in older display devices and GPUs. It has been largely replaced by digital interfaces like HDMI and DisplayPort due to its limited bandwidth and lower image quality.
Advantages:
- Wide compatibility with older devices.
- Simple and inexpensive.
Disadvantages:
- Analog signal prone to interference.
- Limited resolution and image quality compared to digital interfaces.
Compatibility with GPUs
When choosing a display port for your GPU, it’s essential to consider compatibility with both the GPU and the display device. Factors such as connector type, version, and supported features influence compatibility and performance.
Best Display Port for Gaming
For gaming, DisplayPort is generally preferred due to its high bandwidth and support for adaptive sync technologies like AMD FreeSync and NVIDIA G-SYNC. DisplayPort allows for smooth gameplay with high refresh rates and minimal screen tearing, enhancing the gaming experience.
Best Display Port for High-Resolution Displays
For high-resolution displays, such as 4K and 8K monitors, HDMI 2.1 and DisplayPort are the best options. These interfaces offer sufficient bandwidth to support ultra-high resolutions and refresh rates, delivering crisp and detailed images.
Future Trends in Display Ports
As technology evolves, display ports are expected to continue advancing to meet the demands of emerging display technologies. Innovations such as HDMI 2.1a and DisplayPort 2.0 aim to further increase bandwidth and support new features like variable refresh rate (VRR) and dynamic HDR, enhancing the visual experience for users.
How to Choose the Right Display Port for Your GPU
When selecting a display port for your GPU, consider the following factors:
- Compatibility with GPU and display device.
- Required features (e.g., high refresh rates, adaptive sync).
- Future-proofing for upcoming technologies.
- Budget and availability of cables and adapters.
Common Mistakes When Selecting Display Ports
Avoid these common mistakes when choosing a display port:
- Ignoring compatibility between GPU and display device.
- Assuming all display ports offer the same performance.
- Overlooking the need for specific features like adaptive sync.
- Neglecting to check cable and adapter requirements.
Upgrading Your Display Port
If you’re considering upgrading your display port, assess your current setup and requirements to determine if an upgrade is necessary. Factors such as display resolution, refresh rate, and desired features can influence the decision to upgrade to a newer interface like HDMI 2.1 or DisplayPort 2.0.
Conclusion
Choosing the right display port for your GPU is essential for achieving optimal performance and visual quality. By understanding the different types of display ports, their advantages and disadvantages, and compatibility considerations, you can make an informed decision that meets your specific needs and preferences.